


2019 6 doi: 10.3389/ antimicrobial resistance with proven expertise
Diagnostic Bacteriology in District Hospitals in Sub-Saharan Africa: At the Forefront of the Containment of Antimicrobial Resistance. Jacobs J., Hardy L., Semret M., Lunguya O., Phe T., Affolabi D., Yansouni C., Vandenberg O. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Wayne, NJ, USA: 2020.

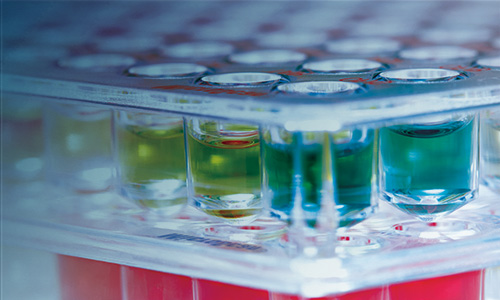
M100: Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Laboratory Medicine in Africa: A Barrier to Effective Health Care. Petti C.A., Polage C.R., Quinn T.C., Ronald A.R., Sande M.A. Clinical bacteriology in low-resource settings: Today’s solutions. Ombelet S., Ronat J.B., Walsh T., Yansouni C.P., Cox J., Vlieghe E., Martiny D., Semret M., Vandenberg O., Jacobs J., et al. MicroScan identification system bacterial identification blood cultures clinical bacteriology low-resource settings. Improvements in stability, robustness, and ease of use have been identified to assure adaptation to LRS constraints. In conclusion, the accuracy of the MicroScan identification panels was excellent for Gram-negative species and good for Gram-positive species. Inoculation of the panels was favorably evaluated, whereas the visual reading of the panels was considered error-prone. The readability level of the IFU was considered too high for LRS. Testing of Gram-positive isolates on Gram-negative panels and vice versa ( n = 144) resulted in incorrect identifications for 38.2% of tested isolates. Of species not represented in the database (e.g., Streptococcus suis and Bacillus spp.), 53.1% out of 49 isolates were incorrectly identified as non-related bacterial species. Of species represented in the MicroScan database, 94.6% (185/195) of Gram-negative and 85.9% (110/128) of Gram-positive isolates were correctly identified up to species level. The ease of use of the panels and readability of the instructions for use (IFU) were evaluated. Robustness was studied by inoculating Gram-negative species on the Gram-positive panel and vice versa. The MicroScan Dried Overnight Positive ID Type 3 (PID3) panels for Gram-positive organisms and Dried Overnight Negative ID Type 2 (NID2) panels for Gram-negative organisms were assessed with 367 clinical isolates from LRS. We evaluated the MicroScan identification panels (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA) as part of Médecins Sans Frontières' Mini-lab Project. 8 Division of Infection and Immunity, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University College London, London WC1E 6BT, UK.īacterial identification is challenging in low-resource settings (LRS).7 Innovation and Business Development Unit, Laboratoire Hospitalier Universitaire de Bruxelles-Universitair Laboratorium Brussel (LHUB-ULB), Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB), 1050 Brussels, Belgium.6 Center for Environmental Health and Occupational Health, School of Public Health, Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB), 1050 Brussels, Belgium.5 Bacteriology-Hygiene Unit, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Bicêtre Hospital, 94270 Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, France.4 Team ReSIST, INSERM U1184, School of Medicine, University Paris-Saclay, 94807 Villejuif, France.3 Médecins Sans Frontières, Operational Center Paris, 75019 Paris, France.2 Immunology & Microbiology Department, KU Leuven, 3000 Leuven, Belgium.1 Department of Clinical Sciences, Institute of Tropical Medicine, 2000 Antwerp, Belgium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
